Should I Enable Windows To Write Caching?
Enable Windows Write Caching is a feature in Windows that can significantly impact your computer’s performance and data security. By caching frequently accessed data, write caching can speed up your system by reducing the time the hard drive needs to be accessed. However, this convenience has a potential downside: if your computer loses power or crashes before the cached data is written to the hard drive, you could lose vital information. This article will explore the pros and cons of enabling write caching and guide when it’s best to turn this feature on or off.
Windows Write Caching: A Quick Overview.
Windows write caching is a feature that can significantly impact your computer’s performance and data security. It works by storing frequently accessed data in a temporary memory buffer, reducing the number of times the hard drive needs to be accessed. This can result in faster system performance, especially when working with large files or programs. However, the convenience of write caching comes with a potential risk. If your computer loses power or crashes before the cached data is written to the hard drive, you could lose vital information.
Enable Windows Write Caching is enabled by default in Windows, but you can turn it off if you’re concerned about the risk of data loss. To turn off write caching, open the Control Panel, click “System and Security,” and then click “Power Options.” In the “Power Options” window, click the “Change plan settings” link next to your current power plan. The “Edit Plan Settings” window, click on the “Change advanced power settings” link. In the “Advanced Power Settings” window, expand the “Hard Disk” section and then expand the “Turn Off Hard Disk After” section. Set the “Turn Off Hard Disk After” value to “Never.” Click the “Apply” button and then the “OK” button.
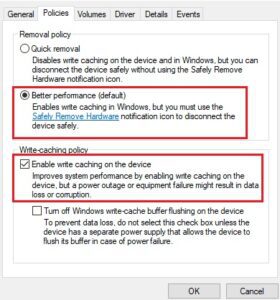
Whether you should turn on or off write caching depends on your needs and preferences. If you’re concerned about the risk of data loss, you should turn off write caching. However, leave write caching enabled if you’re looking for the best possible performance. Ultimately, whether or not to allow write caching is up to you.
Pros Of Enabling Write Caching:
Write caching offers several advantages that can enhance the overall user experience and system performance. Firstly, it significantly improves the responsiveness of your computer by reducing the time taken to access frequently used data. By storing frequently accessed data in the memory buffer, write caching eliminates the need to retrieve it from the slower storage device whenever required. This leads to faster application launches, faster file access, and a smoother computing experience.
Another advantage of write caching is its ability to extend the life of your storage device. By reducing the number of read/write operations performed on the storage device, note caching helps minimize wear and tear, prolonging its lifespan. This becomes particularly beneficial for solid-state drives (SSDs), which have a limited number of write cycles before they start to degrade.
Furthermore, write caching can also improve the battery life of laptops and other portable devices. By reducing the frequency of accessing the storage device, write caching helps conserve power and extend battery life. This is especially useful for users who are on the go and rely on their laptops for extended periods without access to a power outlet.
Overall, write caching provides several advantages that can enhance your computer’s performance, responsiveness, and battery life. While there is a slight risk of data loss during a power failure or system crash, the benefits of write caching often outweigh this risk for most users.
Cons Of Enabling Write Caching
While write caching can provide significant performance benefits, it has drawbacks. One of the main risks of enabling write caching is the increased risk of data loss. It may be lost if the computer loses power or crashes before the data in the cache has been written to the hard drive. This can be a significant concern for businesses or individuals who handle sensitive or critical data.
Another potential downside of write caching is reduced performance in specific scenarios. For example, if the cache becomes full, it can cause the system to slow down as it tries to manage the data in the cache. Additionally, write caching can interfere with specific software applications, particularly those that require real-time data access.
In some cases, write caching can also lead to data corruption. If the data in the cache becomes corrupted, it can cause errors or unexpected behaviour in the operating system or applications. This can be a severe problem, mainly if it affects critical system files or user data.
Finally, write caching can cause problems with certain types of hardware, particularly older devices or those not designed to support note caching. For example, some external hard drives or USB flash drives may not work correctly with write caching enabled.
While write caching can provide significant performance benefits, knowing the potential risks and drawbacks is essential before enabling it. Consider disabling write caching if you are concerned about data loss or other possible issues.
When You Should Enable Write Caching
You should enable write caching if you have a mechanical hard drive (HDD) as your primary storage device. HDDs have slower read/write speeds than solid-state drives (SSDs), so write caching can help improve performance by reducing the time it takes to register data to the hard drive. However, note caching may not provide a noticeable performance benefit if you have an SSD.
Another factor to consider is the frequency of power outages or system crashes. If you rarely or never experience these events, you can safely enable write caching without worrying about data loss. However, if you live in an area with frequent power outages or your computer is prone to crashing, you should turn off write caching to protect your data.
Consider the types of files you work with. If you work with files requiring high levels of data integrity, such as financial documents or medical records, you should turn off write caching to avoid the risk of data corruption. However, you can safely enable write caching if you typically work with less critical files, such as text documents or images.
Finally, it would help if you considered your performance and data integrity priorities. You can enable write caching if you prioritize faster write performance over data integrity and reliability. However, if you are more concerned about protecting your data, you should turn off write caching.
When You Should Turn Off Write Caching
Here is what you asked for:
While Enable Windows Write Caching is generally safe and improves performance for most computers, there are certain situations where it should be disabled. One scenario is if your computer has a solid-state drive (SSD) as its primary storage device. SSDs are much faster than traditional mechanical hard drives (HDDs) and do not benefit from write caching as much. Enabling write caching on an SSD can reduce performance in some cases.
Another situation where you should disable write caching is if you experience frequent power outages or surges. Any data stored in the write cache will be lost when the power goes out. This can lead to data corruption or loss, a severe problem. It is best to turn off write caching to protect your data if you live in an area with frequent power outages.
You should also turn off write caching if you work with files too large to fit into the cache. When a file is too large to fit into the cache, it will be written to the hard drive in multiple passes. This can slow down performance and increase the risk of data corruption. If you work with large files, it is best to turn off write caching to avoid these problems.
Write Caching Using A Software RAID Configuration:
Finally, you should turn off write caching using a software RAID configuration. RAID technology combines multiple hard drives into a single logical drive. When enabled, write caching can interfere with RAID and cause data corruption. If you use RAID, disabling write caching to protect your data is essential.
By following these guidelines, you can determine whether or not write caching is suitable for your computer. In most cases, write caching is safe and significantly boosts performance. However, there are certain situations where it should be turned off to avoid data loss or corruption.

Leave a Reply