How Do I Allow Access To Third Party Cookies
Allow Access To Third Party Cookies In the digital age, cookies have become an integral part of our online experience. These small text files are stored on your device by websites you visit and are used to enhance your browsing experience. However, not all cookies are created equal. Third-party cookies, in particular, have come under scrutiny for their potential impact on user privacy.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of third-party cookies, exploring their purpose, the reasons behind their blocking, and how to allow them in major browsers. We will also uncover the potential downsides associated with third-party cookies and discuss viable alternatives that safeguard your privacy while still enabling a seamless online experience.
What Are Third-Party Cookies?
In the digital landscape, third-party cookies play a significant role in shaping our online experiences. These small text files, placed on your device by websites you don’t directly visit, act as silent observers, diligently tracking your online activities across multiple platforms. Their purpose? To gather data about your browsing habits, preferences, and interactions. This wealth of information serves various purposes, from personalizing advertisements to enhancing website analytics and enabling social media tracking.
Third-party cookies can originate from various sources, including social media platforms, advertising networks, and content delivery networks. Even websites you directly visit may employ third-party services for specific features like embedded videos or social media sharing buttons, leading to the placement of these cookies on your device.
The extensive tracking capabilities of these cookies raise questions about the ethical use of personal data and the potential for unauthorized access or misuse. It’s crucial to be aware of these potential risks and take appropriate measures to protect your privacy when navigating the online world.
Why Are Third-Party Cookies Blocked?
Third-party cookies are blocked for a number of reasons, including to protect user privacy, enhance security, comply with privacy regulations, and improve website performance.
Protecting User Privacy:
Third-party cookies can track users across multiple websites and collect vast amounts of data about their online activities. Many users find this level of tracking to be intrusive and a violation of their privacy. Blocking third-party cookies helps to protect user privacy by preventing websites from tracking users without their knowledge or consent.
Enhancing Security:
Third-party cookies can also be used for malicious purposes, such as phishing attacks and identity theft. By blocking third-party cookies, users can help to protect themselves from these threats.
Complying With Privacy Regulations:
For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires websites to obtain users’ consent before setting third-party cookies. Blocking third-party cookies helps websites to comply with these regulations.
Improving Website Performance:
Third-party cookies can slow down website loading times and negatively impact user experience. By blocking third-party cookies, websites can improve their performance and provide a better user experience.
Overall, blocking third-party cookies provides a number of benefits for users, including protecting privacy, enhancing security, complying with privacy regulations, and improving website performance.
How To Allow Third-Party Cookies In Major Browsers
This section will provide instructions on how to allow third-party cookies in major browsers.
Google Chrome
1. Open the Chrome browser.
2. Click the three-dot menu in the top-right corner of the window.
3. Select “Settings.”
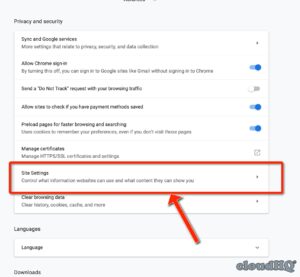
4. Click “Privacy and security.”
5. Under “Cookies and other site data,” click “See all cookies and site data.”
6. Find the website for which you want to allow third-party cookies.
7. Click the “Allow” button next to the website.
Mozilla Firefox
1. Open the Firefox browser.
2. Click the three-line menu in the top-right corner of the window.
3. Select “Options.”
4. Click “Privacy & Security.”
5. Under “Cookies and Site Data,” click “Manage Permissions.”
6. Find the website for which you want to allow third-party cookies.
7. Click the “Allow” button next to the website.
Microsoft Edge
1. Open the Edge browser.
2. Click the three-dot menu in the top-right corner of the window.
3. Select “Settings.”
4. Click “Privacy, search, and services.”
5. Under “Cookies,” click “Choose what you block.”
6. Find the website for which you want to allow third-party cookies.
7. Click the “Allow” button next to the website.
Apple Safari:
1. Open the Safari browser.
2. Click the “Safari” menu in the top-left corner of the window.
3. Select “Preferences.”
4. Click “Privacy.”
5. Under “Cookies and website data,” click “Manage website data.”
6. Find the website for which you want to allow third-party cookies.
7. Click the “Allow” button next to the website.
Opera:
1. Open the Opera browser.
2. Click the “Menu” button in the top-left corner of the window.
3. Select “Settings.”
4. Click “Privacy & security.”
5. Under “Cookies,” click “Manage exceptions.”
6. Find the website for which you want to allow third-party cookies.
7. Click the “Allow” button next to the website.
Potential Downsides To Allowing Third-Party Cookies
Allow Access To Third Party Cookies There are several potential downsides to allowing third-party cookies. One major concern is privacy. Third-party cookies can track users across multiple websites and collect a significant amount of data about their browsing habits and preferences.
Another potential downside is security. Malicious actors can use third-party cookies to gain access to sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details.
Third-party cookies can also impact website performance. This can be particularly problematic for users with slower internet connections or limited data plans.
Alternatives To Third-Party Cookies
There are a number of alternatives to third-party cookies that websites can use to track user activity and collect data. These alternatives include first-party cookies, session cookies, local storage, Indexed DB, and Web Sockets.
Session cookies are temporary cookies that are stored on the user’s computer for the duration of their visit to a website. They are deleted when the user closes their browser. Session cookies can be used to track the user’s activity on a website during a single visit, but they cannot be used to track the user’s activity across multiple visits.
Local storage is a browser-based technology that allows websites to store data on the user’s computer. Local storage is more persistent than cookies, and it can be used to store larger amounts of data. That storage can be used to track the user’s activity on a website across multiple visits, but it is not shared with other websites.
Allows Websites To Store Data:
Indexed DB is a browser-based technology that allows websites to store data in a structured format. Indexed DB is more powerful than local storage, and it can be used to store larger amounts of data. Index DB can be used to track the user’s activity on a website across multiple visits, but it is not shared with other websites.
Web Sockets are a browser-based technology that allows websites to establish a real-time connection with the user’s browser. Web Sockets can be used to track the user’s activity on a website in real time, but they are not shared with other websites.
These are just a few of the alternatives to third-party cookies that websites can use to track user activity and collect data. Each of these alternatives has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice for a particular website will depend on the specific needs of that website.

Leave a Reply