How is Auditing Enabled in Windows
Auditing enabled in Windows is equipped with a feature called “Audit Policy” which logs file access events. This feature is located in the Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Local Policies. Users can enable this feature by clicking on the Advanced Security Settings button. In the next window, select the Auditing tab. In the list that appears, select the “All Users” option. After that, choose the “Audit object access” option and enter a name.
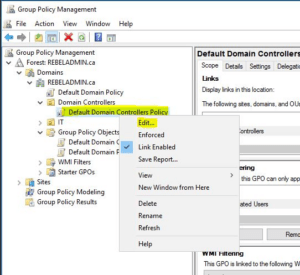
After enabling Auditing, it will log events for every object that changes ownership. This event contains data about the user’s IP address and other details. It also records any network logon sessions. However, a user can disable the feature by closing the Advanced Security Settings for a folder.
When a user requests to access an object, Google Windows will log the event ID 5140. Then, it will log the event if the user has permissions that are flagged for auditing. If the user is denied access, Windows will log an event. If the user’s attempt matches the success or failure criteria of the event, it will be recorded.
Enable Audit Logging Windows Server 2022:
After you’ve enabled auditing, you can enable or disable it for specific objects. You can also specify the types of data that Windows will record for auditing. The auditing policy will log the details of the access. The events can be classified as either “complete” or “noncomplete”. The Auditing policy will determine which files are marked for auditing, and the time period for logging. There is no limit on the amount of data you can log.
The Auditing policy is located in Computer Configuration. You can also use it to track sensitive files. If you want to turn on the auditing feature for a particular file, just click on the corresponding button. Then, you can set the time when you want to see the logs.
How To Enable Audit Policy In Windows Server:
To enable the auditing policy, go to the Security tab in the Control Panel. Locate the Auditing policy and double-click on the corresponding Configuration column. Afterward, select Auditing. Alternatively, you can view audited events in the Events Viewer. Once you have enabled the auditing policy, click on the Local Group Policy Editor, and click on the “Audit” button.
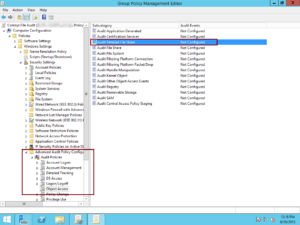
You can also set up advanced auditing to track File System access and the Windows Firewall. Both of these settings will make Windows auditing more effective. When it comes to security, the more you can monitor, the more you can protect your system. You can use these settings to detect and prevent malicious activities in real time. If you don’t like the default setting, you can always turn off the auditing feature.
Auditing Enabled in Windows Start Automaticall:
The File Access subcategory is the most important one for most organizations. You can then set up the auditing policy on individual files or folders. A successful auditing policy will show the number of files accessed by each user. Once you’ve enabled these policies, the process will start automatically. It takes a few seconds to set up, but you can easily customize the Windows settings.
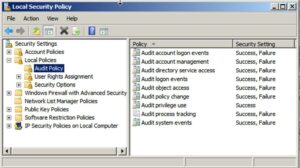
Enable Object Auditing In Windows:
- Navigate to Administrative Tools> Local Security Policy.
- In the left pane, expand Local Policies, and then click Research Policy.
- Select access to the test item in the right pane, then click Action> Properties.
- Choose Success and Failure.
- Click OK.
- Close the Local Security Policy window.
File and folder access auditing is a valuable security feature. It’s possible to turn it on or off. You can also configure it for files. If you want to, you can also set the default auditing policy for folders and files. It’s important to set the auditing policy on every folder and file that you own, because it will help prevent the user from violating the privacy settings of other users.
Leave a Reply