How Do I Enable Wi-Fi Calling Permanently?
Many popular messaging apps use VoIP services to make calls over Wi-Fi. Carrier-branded Enable Wi-Fi Calling Permanently is a feature that’s baked directly into your phone and automatically activates when you lose cellular signal.
However, there are some important differences to understand when enabling this option. Read on to learn more about what WiFi calling is and how it works.
Enable Wi-Fi Calling Permanently on your device can vary slightly depending on the make and model of your smartphone and the carrier you are using. In this guide, I’ll provide you with general instructions that should cover most devices and carriers. Please note that specific steps may differ, so it’s always a good idea to refer to your device’s user manual or your carrier’s support documentation for the most accurate information.
1. Check Compatibility:
Ensure that your smartphone and carrier support Wi-Fi Calling. Most modern smartphones and major carriers offer this feature, but it’s essential to confirm compatibility before proceeding.
2. Update Software: Make sure your device’s operating system is up-to-date. Manufacturers often release updates that include improvements and new features, including enhancements to Wi-Fi Calling. Go to your device settings, find the “Software Update” or “System Update” option, and install any available updates.
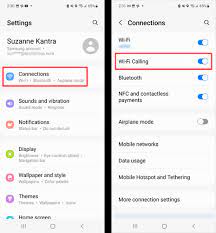
3. Enable Wi-Fi Calling on Android: For Android devices, the steps may vary slightly based on the device manufacturer and Android version, but generally:
- Open the “Settings” app.
- Navigate to “Network & Internet” or a similar option.
- Look for “Wi-Fi Calling” or “Connections” and select it.
- Toggle the Wi-Fi Calling switch to enable the feature.
- Follow any on-screen prompts to complete the setup.
4. Enable Wi-Fi Calling on iPhone: If you are using an iPhone:
- Open the “Settings” app.
- Scroll down and tap on “Phone.”
- Select “Wi-Fi Calling” and toggle the switch to enable it.
- You may need to enter or confirm your emergency address for 911 services.
- Follow any additional prompts to complete the setup.
5. Carrier-Specific Instructions: Different carriers may have specific steps or requirements for enabling Wi-Fi Calling. Contact your carrier’s customer support or visit their official website for detailed instructions. Some carriers might require you to activate Wi-Fi Calling through their dedicated apps or online account portals.
6. Emergency Address: As part of enabling Wi-Fi Calling, you may be required to provide an emergency address. This information is crucial for emergency services to locate you accurately when you make a 911 call over Wi-Fi. Double-check that the address is correct and update it if necessary.
7. Test Wi-Fi Calling: After enabling Wi-Fi Calling, make a test call to ensure that the feature is working correctly. Call quality and performance may vary based on your Wi-Fi network’s speed and stability, so it’s advisable to test it in different Wi-Fi environments.
8. Troubleshooting: If you encounter issues with Wi-Fi Calling, check your Wi-Fi connection, update your device’s software, and verify your carrier’s support documentation for troubleshooting tips. Issues may also be related to specific router settings, so ensure that your Wi-Fi network meets the requirements for Wi-Fi Calling.
9. Battery Life and Data Usage: Keep in mind that enabling Wi-Fi Calling may impact your device’s battery life and consume data if your Wi-Fi network is not unlimited. Monitor your device’s battery usage and review your carrier’s policies regarding data usage during Wi-Fi Calls.
10. Security Considerations: Wi-Fi Calling is generally secure, but it’s essential to use secure Wi-Fi networks to prevent potential security risks. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks without proper security measures.
1. Open the Settings app.
When enabled, WiFi calling routes your phone calls over the Internet rather than over your cellular network. It’s not the same as VoIP, and it doesn’t require a separate app or service. When you place a call or text, your phone will automatically identify the strongest network available and route the call accordingly. In most cases, your carrier will treat Wi-Fi calling as if it were a regular call, meaning you don’t incur any extra fees and that your Wi-Fi call minutes are deducted from your monthly talk and text allotment.
To enable Wi-Fi Calling, open the Settings app on your iPhone or Android device. You may see different options depending on your operating system, but you should find a menu item that looks like Settings, Cellular, or Network & Internet. Once in the menu, look for a Wi-Fi Calling option and toggle it on.
Note that in order to use the feature, your carrier must support it. For example, Verizon only allows it on specific devices and requires that the HD Voice setting — or Advanced Calling on some devices – is also enabled.
If you don’t want to enable Wi-Fi calling, you can still prioritize mobile network over Wi-Fi by going into the settings and changing your Calling preference or Roaming preference. It’s worth checking your carrier’s rules on this before traveling abroad, as astronomical international roaming charges can quickly add up.
2. Go to Cellular / Mobile / Connections.
Most iPhones and some Android phones come with WiFi calling enabled, but it might not be turned on. To check, open the Phone app and swipe down from the top with two fingers to reveal the quick menu. If the toggle button is green, you have WiFi calling turned on. This setting will work only if both your network provider and phone manufacturer support it.
WiFi calling works by boosting your cellular signal when you call or text using the internet. If your carrier supports it, it’s an excellent option if you live in a spotty cell service area or have a limited mobile data plan. It also helps when traveling overseas since it can save you international roaming charges.
However, keep in mind that using your phone over the internet will use cellular data unless you have Airplane mode turned on. And since calls are usually much longer than texts, it can quickly add up to your monthly data limit.
To help you manage your mobile data, you can turn off WiFi calling or limit its usage to only local networks. You can also set the Phone app to use only WiFi or cellular data or even restrict it to a specific network. You can find these settings in the Phone or Settings app, but the exact location might vary depending on your device and carrier.
3. Tap Wi-Fi Calling.
Using Wi-Fi calling can improve your call quality in certain situations, especially when you’re at home or in a room with poor cellular signal. But enabling it permanently can be a waste of battery life.
It works by letting you make and receive HD voice calls, as well as send/receive texts and pictures (MMS) over a WiFi network instead of a cellular one. It’s best used as a backup option for when you don’t have a great cellular signal (such as inside buildings or basements).
When your phone is connected to a WiFi network, it sends voice data over the Internet, which gets processed and routed by the carrier before they deliver it to your device. This helps to reduce lag, and it can also save your phone’s battery life since it doesn’t have to work as hard to get a cellular signal.
You can place calls on your iPhone using Wi-Fi calling by tapping a contact or phone number in Contacts, Messages, Safari, or Apple FaceTime. You can even use it to make or answer an incoming call when you’re on your iPad or Apple Watch. If you’re in the US and need to call 911, your emergency call will automatically use WiFi calling if cellular service is unavailable. Your registered address will be provided to emergency response personnel to help them locate your location.
4. Toggle it on.
Enable Wi-Fi Calling Permanently, your phone will use a Wi-Fi connection to make and receive calls instead of cellular network connections. This feature can be beneficial if you have a limited mobile data plan or don’t want to exceed your monthly data allowance. It also provides a better call quality and may boost your signal in areas with poor coverage.
The downside is that using WiFi calling can consume your data allowance and cause your phone to constantly search for a connection when you are outside of WiFi range. This can drain your battery, especially if you have a large data limit or are using an older router.
Disabling WiFi Calling is a simple process that should be relatively easy on most phones. However, the steps can vary slightly between devices and your carrier. For example, iPhones may have different options in the Settings app than Android devices. Regardless, most devices should allow you to disable the feature through the Settings or Cellular / Mobile / Connections menu. If you have trouble, try contacting your device’s manufacturer or carrier for assistance. Once you have disabled WiFi calling, your phone will use cellular networks to make and receive calls whenever possible. If you have poor cellular network coverage, you can still make calls using other apps like FaceTime, Skype, or WhatsApp.
Conclusion
Enabling Wi-Fi Calling involves navigating through your device’s settings, ensuring compatibility, and following carrier-specific steps. Regularly check for updates, test the feature, and troubleshoot if necessary. Always refer to your device’s user manual and your carrier’s support resources for the most accurate and up-to-date information.

Leave a Reply