How Do I Enable Protected Content in Chrome?
Enable Protected Content In Chrome helps digital media creators maintain control over how their work is consumed. This is a crucial aspect of fostering creativity and innovation. Chrome supports protected content by enabling access to content via a secure origin.
Some websites want to access your device’s microphone and camera. This setting allows you to decide whether or not to let them do so.
Enable Protected Content In Chrome involves configuring various settings to ensure a secure and seamless browsing experience. This process includes managing site permissions, adjusting content settings, and ensuring that your browser is up-to-date. Below is a step-by-step guide in enable protected content in Chrome.
Step 1: Update Chrome
Before configuring any settings, it’s crucial to ensure that your Chrome browser is up-to-date. Updates often include security patches and improvements. To check for updates:
- Open Chrome and click on the three dots in the top-right corner (menu icon).
- Hover over “Help” in the menu.
- Select “About Google Chrome.”
- Chrome will automatically check for updates and install them if available.
Step 2: Check Chrome Components
Some components of Chrome are responsible for handling protected content. Make sure these components are up-to-date:
- In the address bar, enter
chrome://componentsand press Enter. - Look for components like “Widevine Content Decryption Module” and “Adobe Flash Player.”
- If updates are available, click “Check for update” under each component.
Step 3: Adjust Site Settings
Chrome allows you to control site-specific settings, including permissions for protected content. To manage site settings:
- Open Chrome and click on the three dots in the top-right corner.
- Select “Settings.”
- Scroll down and click on “Privacy and security” in the left sidebar.
- Under “Site settings,” you can configure various permissions. For protected content, focus on “Content” and “JavaScript.”a. JavaScript: Make sure JavaScript is enabled, as many websites use it to deliver interactive content.
b. Content: Adjust settings related to cookies, images, and notifications based on your preferences.
Step 4: Manage Cookies
Cookies play a crucial role in handling user authentication and session information for protected content. To manage cookies:
- In the “Privacy and security” section of Chrome settings, click on “Cookies and other site data.”
- Ensure that “Allow all cookies” or “Block third-party cookies in Incognito” is selected based on your preference.
Step 5: Enable Flash (if necessary)
Some older websites still use Adobe Flash for multimedia content. While Flash is being phased out, you may need to enable it for certain sites:
- In the “Privacy and security” section, click on “Site settings.”
- Scroll down to “Content” and look for “Flash.”
- Enable the “Ask first” option or allow specific sites to run Flash.
Step 6: Check SSL/TLS Settings
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are protocols that ensure a secure connection between your browser and the website. To check SSL/TLS settings:
- In Chrome settings, go to “Privacy and security” and click on “Security.”
- Ensure that “Use secure DNS” and “Use secure DNS lookups” are enabled.
- Click on “Advanced security” to check for any unsafe connections or certificates.
Step 7: Verify HTTPS Settings
Always prefer websites that use HTTPS, as it encrypts the data exchanged between your browser and the site. To enforce HTTPS:
- In Chrome settings, go to “Privacy and security” and click on “Security.”
- Enable “Safe Browsing” to protect against dangerous sites.
- Enable “Enhanced protection” for a higher level of security.
Step 8: Manage Pop-ups
Protected content may use pop-ups for authentication or displaying additional information. Adjust pop-up settings:
- In Chrome settings, go to “Privacy and security” and click on “Site settings.”
- Scroll down to “Content” and click on “Pop-ups and redirects.”
- Ensure that the “Blocked” option is selected, or allow pop-ups on specific sites as needed.
Step 9: Utilize Chrome Sync (Optional)
If you use multiple devices, Chrome Sync can help ensure that your settings are consistent across all of them. To enable Chrome Sync:
- In Chrome settings, go to “Sync and Google services.”
- Ensure that “Sync” is turned on, and select the relevant options for syncing.
Step 10: Use a Secure Connection
Ensure that your internet connection is secure, especially when accessing protected content. If you are using public Wi-Fi, consider using a virtual private network (VPN) for added security.
By following these steps, you can enhance the security and functionality of your Chrome browser when accessing protected content. Keep in mind that web technologies are constantly evolving, so staying informed about the latest best practices is essential for a secure online experience.
Protected content refers to digital media that is safeguarded from unauthorized access or piracy.
When content is not protected, it can be copied and distributed without authorization. This can lead to loss of revenue for publishers and creators, as it decreases the value of their intellectual property. Fortunately, there are ways to protect digital media from pirates, including DRM (Digital Rights Management). It also helps to track unauthorized use of content.
DRM is a critical tool for anyone who produces or distributes copyrighted content online. It also makes it easier to identify and respond to piracy, by sending DMCA takedown notices to pirate websites that host your work.
One way to protect your content against piracy is by using watermarks, which act as your digital autograph. These can be transparent and overlayed on your content, making it more difficult for pirates to steal your creations without leaving a trace of their identity. Another method of protecting your content is by using encryption, which scrambles the data in the file so that it appears gibberish to anyone who doesn’t have the decryption key. This is especially useful when paired with secure content delivery methods, which prevents pirates from intercepting your content before it can reach its intended audience.
Protected content is typically associated with streaming services
This is especially true for streaming services, which must protect their content from piracy and other forms of theft. To do this, they use a combination of technologies, including DRM, to prevent unauthorized access.
These technologies prevent the content from being downloaded and copied, thereby protecting the copyright of the content creators and distributors. This helps them to maintain a steady income from their content, and ensures that their customers can always watch the media they want. This is essential for their business model, as streaming services rely on subscription fees to operate.
One of the most common methods used to protect content is DRM (digital rights management) technology, which allows video streaming services to restrict access to their content by limiting which devices can play it. For example, Netflix uses DRM to prevent users from sharing their usernames and passwords with others, or using the same computer to log in to multiple accounts at the same time. In addition to DRM, streaming services may also use a variety of other security measures, such as encryption and IP addresses, to limit access.
Chrome’s content privacy settings allow you to set how your browser handles various types of content. For example, you can decide whether websites should ask your permission to receive desktop notifications, or whether they should take over your screen automatically. You can also choose which sites should be able to run plug-ins outside of the sandboxed environment.
Protected content is protected by copyright laws
Copyright laws are an important tool for authors, artists, and companies to protect their works from infringement and piracy. This protection is vital to ensuring that creators can get the credit and profits that they deserve from their creations. Without it, someone could steal the original work of another person and publish it online, potentially stealing their hard-earned income and reputation. The DMCA also allows for some limited uses of copyrighted material, known as fair use.
In addition, copyright law prohibits mutilation of the original work. For example, if someone makes a copy of a work and alters it in some way (by changing the meaning or by making it look different), then they could be sued for violating copyright.
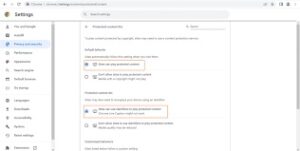
In Chrome, you can set whether websites can disable your mouse cursor while you’re viewing protected content. To do this, go to chrome://settings/content and click on the toggle button next to “Play DRM-controlled content” and “Allow sites to play protected content”. You should also make sure that Widevine is enabled.
Protected content is protected by DRM
Digital rights management (DRM) is a set of technologies that help safeguard copyrighted media. It works by encrypting the data to make it unusable to anyone without a key, and then requiring that the user be verified and/or has permission to get this key. This key is also periodically verified to ensure that the user still has authorization.
DRM can be a controversial topic, with organizations such as EPIC saying it restricts consumer freedom and creates privacy concerns by allowing companies to gather personal information about users.

Leave a Reply