How Do I Turn On My JavaScript?
Many websites require JavaScript to function. From Facebook timelines that automatically update to search engines suggesting words as you type – these are just some examples of dynamic interactions that rely on JavaScript.
To enable JavaScript on your computer browser follow the instructions below for your specific device. It’s easy – and free!
Enabling JavaScript in your web browser is essential for accessing interactive content, dynamic features, and various functionalities on websites. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to enable JavaScript in popular browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
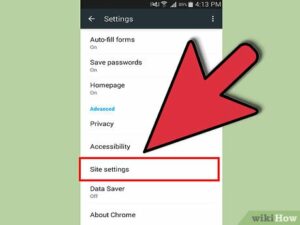
Google Chrome:
- Open Chrome: Launch the Chrome browser on your computer.
- Access Settings: Click on the three dots (menu icon) in the top-right corner of the browser window.
- Go to Settings: Scroll down and click on “Settings.”
- Find Site Settings: In the Settings menu, click on “Privacy and security” on the left sidebar.
- Locate JavaScript Settings: Click on “Site settings.”
- Enable JavaScript: Scroll down and click on “JavaScript.”
- Toggle JavaScript On: Turn on the switch next to “Allowed (recommended)” to enable JavaScript.
Mozilla Firefox:
- Open Firefox: Launch the Firefox browser on your computer.
- Access Options: Click on the three horizontal lines (menu icon) in the top-right corner.
- Go to Preferences: Select “Preferences.”
- Navigate to Privacy & Security: On the left sidebar, click on “Privacy & Security.”
- Enable JavaScript: Scroll down to the “Permissions” section.
- Enable JavaScript: Check the box next to “Enable JavaScript.”
- Confirm Changes: Close the Preferences tab to apply the changes.
Safari:
- Open Safari: Launch the Safari browser on your Mac.
- Access Preferences: Click on “Safari” in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Go to Preferences: Select “Preferences” from the drop-down menu.
- Select Security: Click on the “Security” tab.
- Enable JavaScript: Check the box next to “Enable JavaScript.”
- Close Preferences: Close the Preferences window to save the changes.
Microsoft Edge:
- Open Edge: Launch the Edge browser on your computer.
- Access Settings: Click on the three dots (menu icon) in the top-right corner.
- Go to Settings: Select “Settings” from the menu.
- Navigate to Site Permissions: Click on “Cookies and site permissions” on the left sidebar.
- Select JavaScript: Click on “JavaScript.”
- Enable JavaScript: Toggle the switch to turn on JavaScript.
Important Considerations:
- Keep Browsers Updated: Ensure your browser is updated to the latest version for optimal performance and security.
- Security Risks: JavaScript can pose security risks if not used cautiously. Be mindful of enabling it on trusted websites to prevent potential threats.
- Browser Extensions: Some browser extensions or third-party software might interfere with JavaScript functionality. Disable conflicting extensions if you encounter issues.
Chrome
Google Chrome is a popular web browser that works on computers, laptops, and mobile devices. It syncs your bookmarks, browsing history, and saved passwords across devices so you can access them anytime, anywhere.
To turn on JavaScript in Chrome, click the icon that resembles three small black dots on top of each other on the far right side of your Chrome window. This will display a drop-down menu. Select Settings, then scroll to the bottom of the settings page and click Show advanced settings.
On the Settings page, select the Site settings button under the Privacy group. In the JavaScript section, click the Allow all sites to run JavaScript toggle switch so that it is enabled. Then click OK to save the changes. This should resolve any problems that you are having with websites that have not loaded properly or show an error message. It also should enable the Reading Mode feature of Chrome. This will dismiss all of the extra bits on a page so you can read what’s really important.
Firefox
Firefox is a popular browser among Internet users. Its open source development allows the software to have features that other browsers don’t offer. For example, it can use multiple tabs simultaneously and has a built-in pop-up blocker.
One downside to Firefox is that it may track users more aggressively than other browsers. Those who prefer a less-tracked browsing experience can turn off the browser’s tracking capabilities by clicking Preferences and then Site Settings. Google
For advanced users, Firefox’s about: config page lets you adjust settings that affect how the browser operates. However, changing these settings could affect your browsing experience. If you do make a change, be sure to save the changes before closing the page. Also, if you have any add-ons installed, you may need to disable them or change their settings. The instructions for doing this may vary between the different extensions. Please see the individual add-ons’ websites for more information. In addition, you may need to re-open Firefox and restart it after making the change.
Safari
Apple’s Safari is the default web browser for iPhone and iPad. It features an integrated iCloud feature that syncs passwords, bookmarks, and other information between devices. It also uses Apple’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention functionality to detect and block website tracking.
Safari uses the open-source web engine WebKit and is built into macOS, iOS, and their upcoming VisionOS. It also offers a variety of privacy settings like dark web monitoring and password autofill.
However, many users are enamored with other web browsers like Chrome and Brave for their speed and privacy features. If you’re thinking of ditching Safari, don’t worry, it’s easy to wipe its data and turn it back on if you change your mind. Here’s how:
Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (IE) is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft. It was once the most popular browser, but it lost market share to other browsers such as Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge. IE is still used on some computers, though. Google
The IE browser offers many standard features found on most modern web browsers. For example, it allows users to back and forward through Web pages. It also has the option to refresh the page or session. The IE browser also includes a search box to quickly locate information on a website.
IE has also included unique features such as InPrivate Browsing, which can help users avoid leaving a trail on their computer. The feature can also be useful for those who are concerned about privacy or security issues. In addition, the IE browser can be set to automatically reload certain sites in Internet Explorer mode. This is useful for websites that do not work well with other browsers.

Leave a Reply